Module 30-41
Budget Balance
Difference between what the government spends and what the government brings in.
Major source of income is tax revenue.
Fiscal Policy
Will automatically adjust (automatic stabilizer).
- Government spending
- Tax revenue
Reduce the severity of recessions and inflations.
Monetary Policy
We've talked about RR, Dis. Rate, OMO.
We're now going to apply them towards fixing the economy.
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Increases the money supply to increase aggregate demand.
Increase government spending.
Runs the the budget towards a deficit (as you both are increasing spending as well as decreasing taxes).
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Decreases the money supply to decrease aggregate demand.
Money Market
By shifting the money supply, it changes the interest rate.
Expanding it will reduce the interest rate and make it cheaper to borrow, thus more spending.
Contracting it will increase the interest rate and make it more expensive to borrow, thus less spending.
Interest Sensitive Consumer Spending
Spending that requires a loan.
This will increase when the money supply increases.
Federals Fund Rate
The interest rate banks charge other banks for loans.
Two sources of inflation:
- Cost-Push inflation
- Caused by a significant increase in the cost of inputs.
- Demand-Pull inflation
- Caused by an increase in aggregate demand.
Phillip's Curve
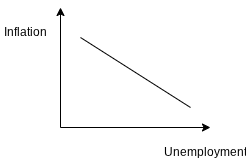
In a Recession
- Government spending will automatically increase
- Because a government will increase its transfer payments.
- Unemployment benefits
- Because a government will increase its transfer payments.
- Tax revenue drops
In an Inflation
- Government spending will automatically drop
- Because a government will decrease its transfer payments.
- Few use unemployment benefits
- Because a government will decrease its transfer payments.
- Tax revenue increases
No, Congress should not be required to run an annual balanced budget.
The budget deficit will increase during recessions, and decrease during periods of economic expansions.
Cyclically adjusted.
Implicit Liability
Spending promised by governments. Not included in our debt statistics.
Inflation
Any change in the MS leads to a long-run change in the aggregate price level.
Inflation Tax
The depreciation in the real value of money as a result of inflation.
Increasing inflation = reduce money holdings.
Hyperinflation - when the price level increase dramatically, drastically.
Causes of Inflation
Cost-push inflation
A leftwards shift of the aggregate supply curve.
Demand-curve inflation
A rightwards shift of the aggregate demand curve.
What type of unemployment that exists in recessionary or inflationary? <- Exit Slip Question
Phillips Curve
A positive demand shock is going to shift you from which point to which point.
Economic Thoughts
Know the people credited with the school of economic thoughts, who was the proponent of it.
Classical:
- Adam Smith
- Laissez Faire - Hands-off policy (from the government)
- Say's Law - Economy is self-correcting.
- Prices are flexible
- Wages adjust
- Interest rates change
Keynesian
- John Maynard Keynes
- In essence, fiscal policy.
- Government has a responsibility to create a demand (all about demand)
- Through taxation and government spending
- President Kennedy was the first.
Monetarism
- Milton Friedman
- Anna Schwartz
- You add to the money supply.
Why is monetary advocated and pursued rather than fiscal? <- Test Question
Monetary makes small incremental changes, fiscal is large and lags.
Short run monetary policy resource question. REserach ample vs limited.
Ample - a lot of excess reserves to loan out, that the money supply is not the issue.
Limited reserves - when banks do not have excess reserves to loan out.
When a country has a banking system with the former, the type that will be used will be administrated interest rates.
With limited, the key tool is open market operations.
Current Account
Tracks all transactions of goods and services.
Financial Account
Tracks all money that comes in and out of the country as it is invested in assets (financial assets).
Exchange Rates
Currencies are traded in the foreign exchange market. The prices at which currencies trade are known as exchange rates.
Appreciation: Goes up in value compared to the other.
Depreciation: Goes down in value compared to the other.
Thus, one will always be appreciating, and the other depreciating.
Equilibrium Exchange Rate is determined by the supply and demand for a specific currency.
Houses count towards the Financial Account!
Foreign Exchange
Reasons there is demand for foreign currency
- Travel & Tourism
- Goods and Services
- Purchase Financial Assets
Any increase in demand of a nation's currency will shift the curve to the right (and vise versa).
Exchange rate is on the y-axis.
Always put the currency you are analyzing in the denominator (i.e. what's on the x-axis, quantity of _'s money).
The supply of currency is determined by governments.
Exchange rate regime
Fixed exchange rate - when the government sets it
Floating exchange rate - when the market sets it

No comments to display
No comments to display