Warm-Ups
Warm-up One:
What does scarcity mean?
Something is scarce when it is desirable and limited. Scarcity occurs because people have unlimited wants, but limited resources to satisfy those wants.
What is the opportunity cost of taking an all expense Hawaii Vacation for Spring Break?
Opportunity cost is the "next best thing" that is given up when a decision is made. In this scenario, the opportunity cost could be a vacation with your family instead.
Identify the Normative Statement
- Inflation is not good for the economy
- Low unemployment is a good thing
- The government should pay for all junior college education
A positive statement has a definite, factual answer, and frequently features the word "is."
A normative statement does not have a definite answer, factual answer, and frequently features the word "should."
The normative statement is: The government should pay for all junior college education.
What is the labor force of the U.S. composed of?
The labor force is composed of the sum of those who are employed and unemployed. Or, in other words, those who are working for pay, and those who are looking for a job.
It excludes active duty, underaged, and those who are not seeking employment.
What does the business cycle illustrate for the U.S.?
The business cycle illustrates the movement of the economy, following its expansions, contractions (recessions), troughs, and peaks.
Warm-up Two:
Illustrate the circular flow of economic activity accurately. Explain the two markets within the economy and what each is doing.
Resource Markets:
Scarce resources owned and provided by consumers. They feature the Factors of Production: Capital, Entrepreneurship, Land, and Labor. It provides the resources for producers to produce goods and services.
Goods and Services
Provides the resources for consumers to produce the factors of production.
Warm-up Three:
Write a one page response summarizing a real-life event where you were in an economic situation. Be sure to highlight each of the lessons and how they played out in your real-life situation.
I had to find a solution for storing our family photos and videos. The primary scarcities were cost and time.
For this, I had two main choices: Use an existing online service, or to build my own local solution.
An online service required little time, but a great amount of monetary cost.
A local solution required a great amount of time, but far less monetary cost.
I ultimately went with the local solution, having the opportunity cost of time that could’ve been spent on other productive activities such as enjoying my winter break (which was at the time).
Warm-up Four:
What are the key economic concepts displayed in a PPC or PPF?
Scarcity, opportunity costs, trade-offs, and efficiency.
What does an outward shift of the curve represent?
Economic growth.
What does an inward shift of the curve represent?
Economic recession.
What does a point inside the curve represent?
Inefficient production.
Is a point outside of the curve possible under current circumstances?
No, because it is considered infeasible.
Warm-up Five:
What are the factors that would cause the demand curve to shift to the left for sweatshirts?
Consumer income (decreases), consumer tastes (decreases), substitutes (other decreases), number of consumers (decreases), complementary goods (other increases in price), price (decreases), and future expectations (future price increases).
If an increase in the price of gasoline results in a decrease in the demand for car tune-ups; what can we assume about the two goods and services?
They are complementary goods.
Assuming pizza is a normal good, an increase in income will do what to the demand for pizza?
The demand will increase because demand for normal goods are proportional to income.
If an increase in the price of string cheese leads to an increase in the demand for cheese sticks, what can we assume about the two products and which way would the demand curve shift for cheese sticks?
We can assume these products are supplementary, and the cheese sticks will shift towards the left.
When lumber costs fall, what happens to the supply of new construction?
The supply will increase due to a reduction in I: Input costs for producer.
A flood on the Oxnard Plain destroys the strawberry crop. What will happen to the supply of strawberries and what will happen to the price of strawberries at the market?
Supply will decrease due to W: Catastrophic weather event. The price will increase.
Draw a graph representing the market for semiconductors in the United States and show what happens when the government imposes a quota on imported semiconductors from Taiwan.
The supply curve will shift towards the left as supply decreases.
Draw a graph representing the market for electric cars in California and show what happens when a new technology reduces the cost of battery production.
The supply curve will shift towards the right as supply increases.
Warm-up Seven:
1. Who buys in the product market? What are they buying?
Households buy from the product market. They buy goods and services.
2. Who sells in the product market? What are they selling? What is their income called?
Firms sells in the product market. They sell goods and services. Their income is called revenue.
3. Who buys in the factor market? What are they buying?
Firms buy in the factor market. They buy the factors of production (land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship).
4. Who sells in the factor market? What are they selling? What is their income called?
Households sells in the factor market. They sell the factors of production (land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship). Their income is called wages, rent, profit, and interest.
Money is always clockwise (on the inside). Factors and services will always be moving counterclockwise.
Warm-up Eight:
- List and describe the three economic goals of a market economy.
1> Sustained long run economic growth.
This describes maintaining a consistent, positive rate of growth.
2> Low unemployment ~4%
This describes maintaining a workforce that is large enough such that the economy is running efficiently, but maintaining a large enough labor pool such that economic expansion is possible through pulling from the labor pool.
3> Keep prices stable ~2-3% inflation.
Keeping prices stable prevents prices from outpacing consumer spending. Otherwise, the purchasing power of consumers could collapse, dramatically slowing the economy.
- What is the importance of calculating GDP?
Compare our economic growth.
Determine if our economic policies are effective.
- Why is low unemployment a desired goal?
Low unemployment enable the economy to operate efficiently.
- Why is inflation above 4% a bad thing?
Inflation above 4% means the average price of goods is increasing substantially per year. This can outpace household spending power, leading to a decline in the economy.
- In the circular flow diagram, what do firms and businesses supply to households? What do households supply to businesses?
Firms and businesses supply goods and services to households. Households supply factors of production for businesses.
- What are the four components of GDP? What category does the construction of new homes and office buildings fall in?
The four components of GDP are: CIGXn - Consumer spending, Investments, Government spending, and net exports.
The construction of new homes and office buildings fall into investments.
Warm-up Ten:
A country has a working age population of 250 million, 185 million people with jobs, and 15 million people unemployed and seeking employment.
- What is the labor force? What is the labor force participation rate? What is the unemployment rate?
How can the UE rate be overstated? Understated?- Labor force = 185 million + 15 million = 200 million. Labor force participation rate = 200 million / 250 million = 80%.
- Unemployment rate = 15 million / 200 million = 7.50%.
- The unemployment rate can be overstated because the unemployment rate includes those who are easily employable, but are unemployed because they are searching for the right job.
- The unemployment rate can be understated because it excludes discouraged workers, under-employed individuals, and marginally attached workers.
- What is the relationship between the business cycle and employment?
- Employment has a proportional relationship with the business cycle. When the business cycle is in an expansion or peak, employment is high; when the business cycle is in a contraction or trough, the employment is low.
- It is inversely proportional to cyclical unemployment.
- Employment has a proportional relationship with the business cycle. When the business cycle is in an expansion or peak, employment is high; when the business cycle is in a contraction or trough, the employment is low.
Warm-up Eleven:
-
How do you calculate the natural rate of unemployment?
The natural rate of unemployment is the sum of structural and frictional unemployment.
-
What factors can increase/decrease the natural rate of unemployment?
Efficiency wages, minimum wages, unions, government policies, subsidies, and an increase or decrease in the number of jobs can all increase or decrease the natural rate of unemployment.
Add. Internet-based job search, job training.
-
Jeff was recently laid off from his job. He looked for work for 3 months and found nothing suitable. He now volunteers at a food bank. What is he classified as?
He is classified as out of the labor force/a discouraged worker because he is not receiving a wage for his contributions nor is he actively looking for a job.
-
Jasmine recently quit her job at the local bakery and has been browsing the internet for jobs, but hasn’t found anything that matches her skills? What is she classified as?
She is classified as frictionally unemployed due to the mismatch of skill and skill demanded.
Warm-up twelve:
- If the MPC is 0.6 and the government increases spending by 1.2 trillion, what will be the change in rGDP?
rGDP = multiplier * change in spending
= 1/(1-0.6) * change in spending
= 1/0.4 * change in spending
= 3 trillion dollars
- Suppose the consumer spending increases by 25 billion, and as a result the equilibrium income (GDP) increases by 125 billion. What is the value of the MPC.
rGDP = 1/(1-MPC) * change in spending
125 = 1/(1-MPC) * 25
5 = 1/(1-MPC)
1/5 = 1-MPC
MPC = 4/5 = 0.8
- Frederico earns $90,000 at his job. He gets a $6,000 raise. What % raise did he receive? When he was given this raise, his spending want from 90,000 to 92,000. Calculate Frederico's MPC and MPS.
% raise = (96000-90000)/90000 = 6.67%
MPC = 2000/6000 = 1/3 = 0.33
MPS = 1-MPC = 0.67
- What does the consumption function show us? What will shift the consumption function upward?
The consumption function shows the relationship between disposable income and consumer spending. If your disposable income increases, you consumer spending will also increase.
Two factors shift the consumption function: Changes in wealth, and changes in expectations of future income.
Warm-up Thirteen:
- What is the interest rate effect on Aggregate demand in response to a change in the aggregate price level in the economy?
The interest rate effect helps prove the aggregate demand curve is downwards sloping. i.e. when the price level decreases, the aggregate demand increases.
This is because an increase an in price level leads to a lower purchasing power for individuals. This causes individuals to increase their money holdings, and thus increase interest rates (by making less money available to be loaned). This in turn decreases the incentive to do investment spending, and thus causes a negative sloping curve.
The other effect, the wealth effect, is because an increase in price level leads to a lower purchasing power for individuals, they are less likely to do consumer spending. This in turn causes the associated negative sloping curve.
An increase in the aggregate price level, results in an increase in the demand of money, which in turns increases the interest rate, which in turn in turn decreases consumer spending, and thus the aggregate output decreases.
- Draw a correctly labeled graph to show the impact of an increase in wealth on aggregate demand.
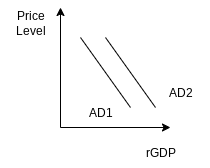
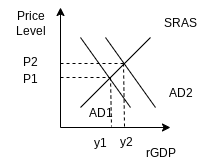
- What happens to the quantity of aggregate output demanded when the price level falls?